Allergen
Nickel
Not just an allergen or a top allergen, nickel is frequently the number one common allergen on published allergen lists, and was the 2008 Allergen of the Year of the American Contact Dermatitis Society.
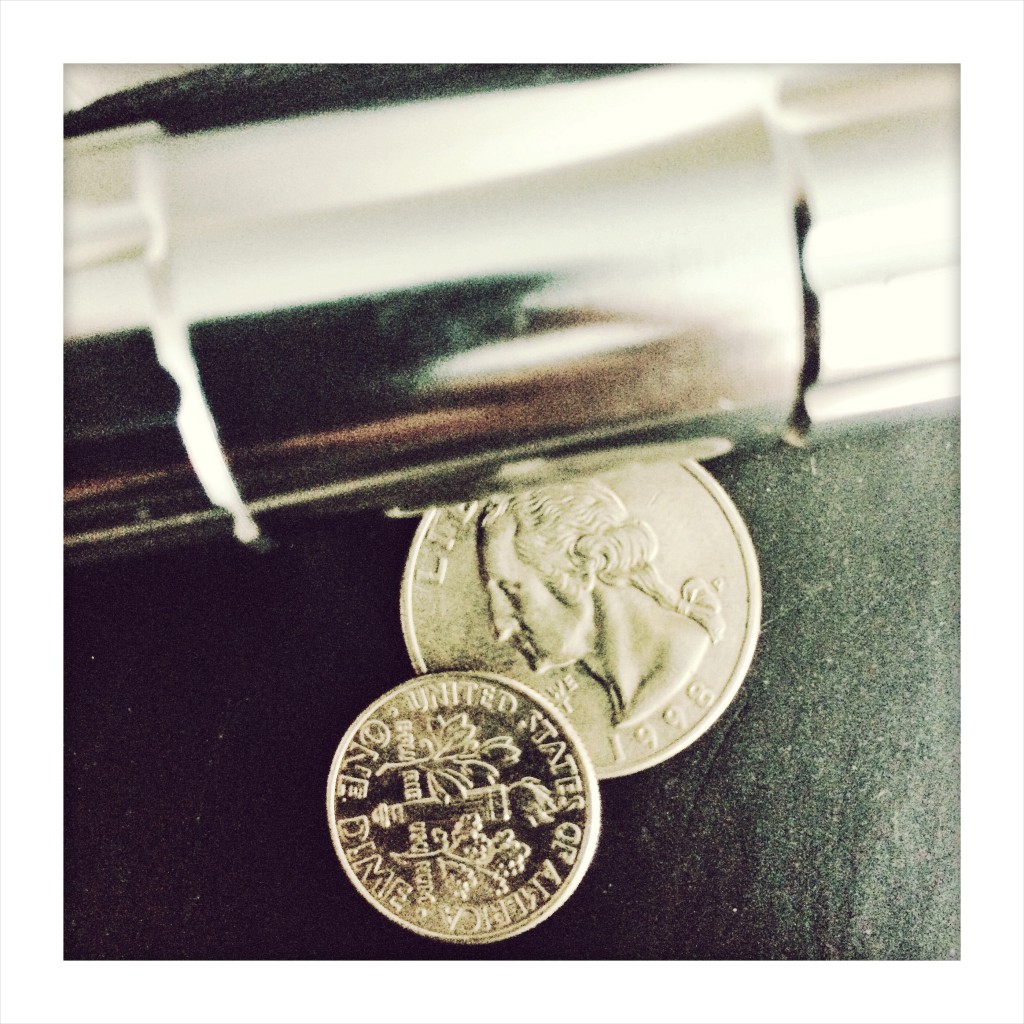
Watch for it in coins; chromed faucets, handles or armrests; certain eyeglass frames or parts, mobile phones or their cases, laptops and other electronics, cosmetic containers, fabrics (invisible as chemicals added to help dyes bind better), cutlery, cooking instruments, dental items, and even many foods and some makeup shades.
Quality (a Strong Bond) Matters
It is very rare for metals not to have some nickel in them. If you are allergic, look for very high-quality metals such as high-end stainless steel — because the nickel tends to be bonded extremely well, the chances of it rubbing off and causing a reaction are minimized.
In very high-quality metals, with the nickel well bonded, the chances of the nickel being rubbed off is significantly reduced. This is important because nickel is dissolved by sweat (a “microbial corrosion”), resulting in its absorption and penetration into the skin, which is what causes the allergic reaction.
What To Do?
- Whenever possible, choose materials that aren’t made with metal. Be guided by your patch test results.
- If you have to use something with metal, try to choose high-quality stainless steel.
- Use fragrance-free, dye-free, paraben-free, preservative-free, allergen-free everything, from skincare to makeup, laundry detergent, household cleaning products, clothing, and more. The last thing we want is a compromised barrier layer that could make your skin more sensitive to allergen exposure. Be guided by your patch test results so you know exactly what you need to avoid.
- If you need to handle or come into contact with something containing nickel, wear white or uncolored, pure cotton gloves. Apply mineral barrier-protective product like Stay-On-Point! or Armada Baby or Post-Procedure thickly on exposed skin. Try doing the work in shorter spurts to limit your exposure. Bathe immediately after and follow with your layered barrier-repairing and protective skincare products.
- If you’ve patch tested positive for nickel, try using a nickel and cobalt spot test on the item you’re considering, especially on the surfaces where you’ll be coming into contact with the metal the most. There are a growing number of tests and barrier creams that block nickel and cobalt ions like Nickel Alert and Nik-L-Block (which also has solutions for cobalt). Just make sure to check the ingredients list — while most are fragrance-free, some may contain preservatives or other allergens (check the ingredients against your patch test results to be safe).
- Talk to both your dermatologist and allergist about other treatment and management options.
If you have a history of sensitive skin…
…don’t guess! Random trial and error can cause more damage. Ask your dermatologist about a patch test.
To shop our selection of hypoallergenic products, visit vmvhypoallergenics.com. Need help? Ask us in the comments section below, or for more privacy (such as when asking us to customize recommendations for you based on your patch test results) contact us by email, or drop us a private message on Facebook.
For more:
- On the prevalence of skin allergies, see Skin Allergies Are More Common Than Ever.
- For the difference between irritant and allergic reactions, see It’s Complicated: Allergic Versus Irritant Reaction.
- For the difference between food, skin, and other types of reactions: see Skin & Food Allergies Are Not The Same Thing.
- On the differences between hypoallergenic, natural, and organic, check out Is Natural Hypoallergenic? and this video in our YouTube channel.
- To learn about the VH-Rating System and hypoallergenicity: What Is The Validated Hypoallergenic Rating System?
Main References:
Regularly published reports on the most common allergens by the North American Contact Dermatitis Group and European Surveillance System on Contact Allergies (based on over 28,000 patch test results, combined), plus other studies. Remember, we are all individuals — just because an ingredient is not on the most common allergen lists does not mean you cannot be sensitive to it, or that it will not become an allergen. These references, being based on so many patch test results, are a good basis but it is always best to get a patch test yourself.- DeKoven JG, Warshaw EM, Reeder MJ, Atwater AR, Silverberg JI, Belsito DV, Sasseville D, Zug KA, Taylor JS, Pratt MD, Maibach HI, Fowler JF Jr, Adler BL, Houle MC, Mowad CM, Botto N, Yu J, Dunnick CA. North American Contact Dermatitis Group Patch Test Results: 2019-2020. Dermatitis. 2023 Mar-Apr;34(2):90-104. doi: 10.1089/derm.2022.29017.jdk. Epub 2023 Jan 19. PMID: 36917520.
- Uter W, Wilkinson SM, Aerts O, Bauer A, Borrego L, Brans R, Buhl T, Dickel H, Dugonik A, Filon FL, Garcìa PM, Giménez-Arnau A, Patruno C, Pesonen M, Pónyai G, Rustemeyer T, Schubert S, Schuttelaar MA, Simon D, Stingeni L, Valiukevičienė S, Weisshaar E, Werfel T, Gonçalo M; ESSCA and EBS ESCD working groups, and the GEIDAC. Patch test results with the European baseline series, 2019/20-Joint European results of the ESSCA and the EBS working groups of the ESCD, and the GEIDAC. Contact Dermatitis. 2022 Oct;87(4):343-355. doi: 10.1111/cod.14170. Epub 2022 Jun 24. PMID: 35678309. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35678309/
- DeKoven JG, Silverberg JI, Warshaw EM, Atwater AR, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group Patch Test Results: 2017-2018. Dermatitis. 2021 Mar-Apr 01;32(2):111-123.
- DeKoven JG, Warshaw EM, Zug KA, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group Patch Test Results: 2015-2016. Dermatitis. 2018 Nov/Dec;29(6):297-309.
- DeKoven JG, Warshaw EM, Belsito DV, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group Patch Test Results 2013-2014. Dermatitis. 2017 Jan/Feb;28(1):33-46.
- Warshaw, E.M., Maibach, H.I., Taylor, J.S., et al. North American contact dermatitis group patch test results: 2011-2012. Dermatitis. 2015; 26: 49-59.
- W Uter et al. The European Baseline Series in 10 European Countries, 2005/2006–Results of the European Surveillance System on Contact Allergies (ESSCA). Contact Dermatitis 61 (1), 31-38.7 2009.
- Wetter, DA et al. Results of patch testing to personal care product allergens in a standard series and a supplemental cosmetic series: An analysis of 945 patients from the Mayo Clinic Contact Dermatitis Group, 2000-2007. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010 Nov;63(5):789-98.
- Warshaw EM, Buonomo M, DeKoven JG, et al. Importance of Supplemental Patch Testing Beyond a Screening Series for Patients With Dermatitis: The North American Contact Dermatitis Group Experience. JAMA Dermatol. 2021 Dec 1;157(12):1456-1465.
- Verallo-Rowell VM. The validated hypoallergenic cosmetics rating system: its 30-year evolution and effect on the prevalence of cosmetic reactions. Dermatitis 2011 Apr; 22(2):80-97.
- Ruby Pawankar et al. World Health Organization. White Book on Allergy 2011-2012 Executive Summary.
- Misery L et al. Sensitive skin in the American population: prevalence, clinical data, and role of the dermatologist. Int J Dermatol. 2011 Aug;50(8):961-7.
- Warshaw EM1, Maibach HI, Taylor JS, Sasseville D, DeKoven JG, Zirwas MJ, Fransway AF, Mathias CG, Zug KA, DeLeo VA, Fowler JF Jr, Marks JG, Pratt MD, Storrs FJ, Belsito DV. North American contact dermatitis group patch test results: 2011-2012.Dermatitis. 2015 Jan-Feb;26(1):49-59.
- Warshaw, E et al. Allergic patch test reactions associated with cosmetics: Retrospective analysis of cross-sectional data from the North American Contact Dermatitis Group, 2001-2004. J AmAcadDermatol 2009;60:23-38.
- Foliaki S et al. Antibiotic use in infancy and symptoms of asthma, rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in children 6 and 7 years old: International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood Phase III. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009 Nov;124(5):982-9.
- Kei EF et al. Role of the gut microbiota in defining human health. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2010 Apr; 8(4): 435–454.
- Thavagnanam S et al. A meta-analysis of the association between Caesarean section and childhood asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008;38(4):629–633.
- Marks JG, Belsito DV, DeLeo VA, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group patch-test results, 1998 to 2000. Am J Contact Dermat. 2003;14(2):59-62.
- Warshaw EM, Belsito DV, Taylor JS, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group patch test results: 2009 to 2010. Dermatitis. 2013;24(2):50-99.
- Verallo-Rowell V. M, Katalbas S.S. & Pangasinan J. P. Natural (Mineral, Vegetable, Coconut, Essential) Oils and Contact Dermatitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 16,51 (2016) . https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-016-0630-9.
- Park G, Oh DS, Lee MG, Lee CE, Kim YU. 6-Shogaol, an active compound of ginger, alleviates allergic dermatitis-like skin lesions via cytokine inhibition by activating the Nrf2 pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016 Nov 1;310:51-59. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2016.08.019. Epub 2016 Aug 22. PMID: 27562088.
- de Groot AC. Monographs in Contact Allergy, Volume II – Fragrances and Essential Oils. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group; 2019.
- De Groot AC. Monographs in Contact Allergy Volume I. Non-Fragrance Allergens in Cosmetics (Part I and Part 2). Boca Raton, Fl, USA: CRC Press Taylor and Francis Group, 2018.
- Zhu TH, Suresh R, Warshaw E, et al. The Medical Necessity of Comprehensive Patch Testing. Dermatitis. 2018 May/Jun;29(3):107-111.